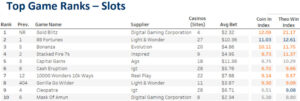
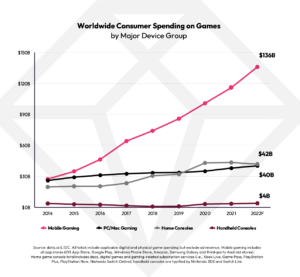
In our household, we have a room affectionately known as the “COD room.” It’s a space where my children and I have spent countless hours playing Call of Duty. Later, against my better judgment, we relented to allowing my middle child to have an Xbox in his room. I often walked by, reminding him that these hours spent gaming were doing nothing for his future employment prospects. I was wrong.
Not only did he meet someone online who referred him to his first job as a software engineer, but those hours were also developing important skills that would prove invaluable in his professional life. A recent study from Finland (Törhönen, 2024) has documented the significant impact of gameplay on work-related skills—a revelation that holds importance for both hiring companies and parents.
Cognitive Abilities
One of the most notable findings from the study is the enhancement of cognitive competences through gaming. Specifically, over half (53%) of the respondents reported that gaming had significantly affected the development of their problem-solving skills. An additional 42% believed it had some effect, meaning that a remarkable 96% perceived a positive correlation between playing video games and their ability to solve complex problems.
Moreover, the ability to quickly adopt and use new software, as well as understand the big picture, were skills that over 30% of respondents felt had significantly improved due to gaming. These are crucial competences in today’s fast-paced, technology-driven work environments.
Gaming also appears to enhance focus, learning, adaptability, and attention to detail. These competences are highly connected to video games, especially those that require players to allocate attention effectively, learn and memorize new information, adapt to unpredictable situations, and process visual details quickly.
However, when it comes to creativity, the impact is less pronounced. The current view suggests that while creativity can be developed, most games do not allow for true creative expression. Instead, they often focus on problem-solving within the constraints of the game’s tools and environment.
Motivational and Emotional Abilities
The study also highlights how gaming can bolster motivational and emotional competences. “Learning from failure” and “persistence/perseverance” were the top-scoring competences in this category. With 41.8% of respondents indicating a significant effect and 49.1% indicating some effect, learning from failure emerged as a key skill developed through gaming.
Persistence and perseverance are closely related, reflecting continuous effort and the desire to complete tasks—a mindset often nurtured in gaming environments where challenges must be repeatedly attempted before success is achieved. Withstanding pressure also scored well, underscoring how gaming can help individuals cope with stress and high-pressure situations.
Social Skills
When it comes to social skills, the impact of gaming is mixed. Empathy received low scores, which can be attributed to several factors. Competitive multiplayer games often encourage a “killer instinct” and may not facilitate empathetic interactions, especially when communication is limited. Additionally, it can be challenging to feel empathy toward non-player characters (NPCs) in single-player games.
On the other hand, teamwork and communication skills were rated highly. Teamwork received significant positive feedback, with 47.3% of respondents noting a significant effect and 41.8% noting some effect on its development through gaming. Effective teamwork is essential for success in many multiplayer games, whether they involve player-versus-environment (PvE) or player-versus-player (PvP) scenarios. Communication is a critical component of this teamwork, enabling players to coordinate strategies and achieve common goals.
Conclusion
Recognizing the professional skills nurtured through gaming reshapes our understanding of its role in personal development. The Finnish study highlights that video games are more than entertainment; they are platforms where essential competences like problem-solving, adaptability, perseverance, and teamwork are honed. For parents, this insight encourages a supportive stance toward their children’s gaming pursuits, seeing them as opportunities for growth rather than distractions. Employers, too, can raise their expectations on the likely presence of game-related skills in candidates and spend more attention evaluating differentiating skills. Embracing the positive impact of game play opens avenues for enriching both individual careers and organizational dynamics.
For parents and hiring companies, these insights offer a new perspective on the value of gaming. Rather than dismissing it as a mere pastime, recognizing the potential for skill development can lead to more supportive environments at home and more informed hiring practices in the professional sphere.
About the author:
Michael Lee, a former Accenture senior executive, raised three kids two of whom are avid gamers who ended up in global technology companies. Michael is currently the Managing Director of QDStaff, a talent consulting and recruiting firm for mobile game studios whose clients include the world’s leading iGame creators.
Reference
Törhönen, J. (2024). Professional competence as a by-product of gaming-as-a-hobby: A descriptive survey study. Master’s thesis, University of Turku. Retrieved from University of Turku Repository.